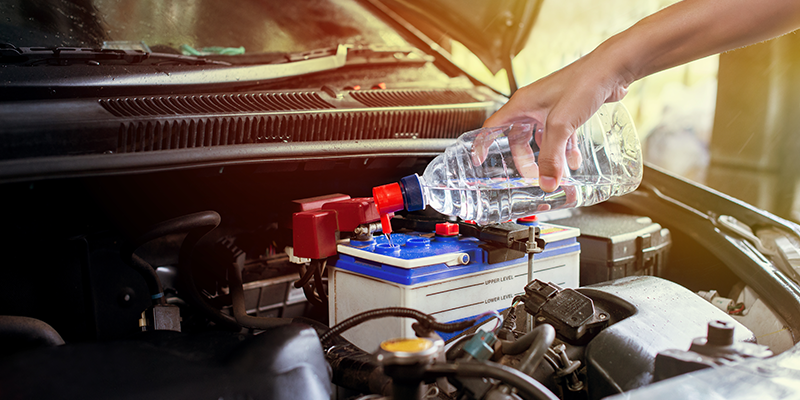
Why is Distilled Water Used for Batteries?
Distilled water is a critical component in maintaining and operating certain types of batteries, particularly lead-acid batteries. This is because distilled water is free from impurities, minerals, and contaminants that can interfere with the chemical processes inside a battery. Impurities like calcium, magnesium, and iron in tap water can accumulate on battery plates, reducing efficiency, capacity, and lifespan. Additionally, impurities may cause corrosion, further damaging the battery’s internal components. Using distilled water, battery owners ensure the electrolyte solution remains balanced, preserving the battery’s ability to store and deliver energy effectively.
Batteries operate on a delicate electrochemical reaction where water plays a pivotal role. During the charging process, water within the electrolyte solution can evaporate or split into hydrogen and oxygen gases, requiring periodic replenishment. Using distilled water prevents the introduction of foreign elements, keeping the chemical integrity of the battery intact and ensuring optimal performance over time.
What Kinds of Batteries Use Distilled Water?
The primary type of battery that requires distilled water is the lead-acid battery, a long-standing technology used for various applications. Lead-acid batteries come in two main varieties: flooded and sealed. Flooded lead-acid, wet-cell batteries require regular maintenance, including checking and topping off the water level with distilled water.
Gel and absorbed glass mat (AGM) sealed lead-acid batteries do not require water maintenance. However, for flooded batteries, neglecting to use distilled water can lead to sulfation of the plates, reducing the battery’s lifespan and efficiency. Other types of batteries, such as lithium-ion or nickel-metal hydride, do not require distilled water since they are sealed and operate using different chemistries.
What Types of Equipment or Vehicles Might Use Distilled Water for Batteries?
Distilled water is commonly associated with the maintenance of lead-acid batteries used in a wide range of equipment and vehicles. Automobiles, for instance, often rely on lead-acid batteries for starting, lighting, and ignition (SLI) purposes. Regular maintenance, including adding distilled water to the battery’s electrolyte, can extend its life and improve reliability.
Electric golf carts also use lead-acid batteries, particularly the flooded type, to power their motors. Regularly adding distilled water is crucial to maintaining the electrolyte balance and ensuring consistent performance on the golf course. Similarly, widely used in warehouses and industrial settings, forklifts rely on lead-acid batteries for heavy-duty operation. Keeping these batteries in top condition often includes the use of distilled water.
Another significant application is in renewable energy systems, such as solar panels or wind turbines. Off-grid solar installations frequently employ deep-cycle lead-acid batteries to store energy generated during the day for use at night. These batteries, including distilled water, require meticulous maintenance to maximize their storage capacity and longevity. Marine vessels, recreational vehicles (RVs), and backup power systems also commonly use lead-acid batteries that benefit from the addition of distilled water.
What Other Industries Use Distilled Water?
Beyond its application in battery maintenance, distilled water is vital in numerous industries due to its purity. The medical and pharmaceutical fields rely on distilled water for applications such as sterilization, preparation of medicines, and laboratory experiments. The absence of contaminants ensures the accuracy and safety of sensitive processes.
Distilled water is used in manufacturing processes like cooling and cleaning. High-precision industries, such as electronics and semiconductors, depend on distilled water for rinsing components to avoid contamination that could compromise product integrity. In the food and beverage industry, distilled water is used for cleaning equipment and as an ingredient in products where purity is paramount.
Distilled water is also essential in cosmetics production, serving as a base for creams, lotions, and other products. The automotive industry uses distilled water for batteries and cooling systems to prevent mineral buildup in radiators. Research laboratories and educational institutions also use distilled water for experiments and chemical preparations.
Distilled Water Has Many Uses!
Using distilled water for batteries ensures the efficient operation and extended lifespan of lead-acid batteries, widely used in vehicles, golf carts, solar energy systems, and more by providing a pure, contaminant-free solution. Its role in maintaining electrolyte balance and preventing internal damage makes it indispensable for those relying on these batteries.
Moreover, distilled water’s utility extends beyond batteries, serving critical functions in healthcare, manufacturing, and food production industries. This versatility underscores its value across numerous applications. For anyone managing equipment or systems reliant on lead-acid batteries, distilled water is a simple yet effective practice that safeguards performance and durability. Distilled water remains a cornerstone of reliable operation, whether in vehicles, renewable energy setups, or industrial machinery.